What is CFD trading and how does it work?
CFD stands for Contracts For Difference . CFD trading means that you are going to trade in the price of the financial instruments. With this form of trading, you do not trade in the financial instrument itself and you do not own the instrument itself. When trading in CFDs, you do not have to pay the full costs immediately, which means that you can take a larger position on the CFD market with the same amount of money than when you invest in the instrument itself. When you invest in the instrument itself, 9 times out of 10 you do have to pay the full costs before you get your hands on the instrument. But how does this work? In this article we will discuss what CFD trading entails, how this form of investing works and what you can pay attention to in order to limit your risk.
What is ‘CFD trading’?
What is ‘CFD trading’ anyway? With CFD trading you trade in CFDs. This means that you buy and sell these CFDs. Now we still don’t really know much. Simply put, with CFDs you trade in the prices on the financial markets. This means that you mainly focus on the price fluctuations of a certain financial instrument , because you can make a profit or loss based on these price fluctuations.
You can trade in all kinds of different underlying instruments, such as shares , commodities or indices.
CFD trading: how it works
With a CFD you get the difference between the price that applies at the moment you conclude the contract and the price at which you terminate the contract. This difference can be both positive and negative: you make a profit or a loss. When trading in CFDs it is therefore very important that you can predict price movements well and keep a close eye on the market. These price movements ensure that you make a profit or not.
If you want to start trading CFDs, it is useful to know that you can use a CFD to respond to both a price increase and a decrease. Responding to an increase is also called ‘ going long ‘. Responding to a decrease is also called ‘ going short ‘.
Imagine: you expect the shares of company X to fall. Then it is beneficial to go short at this moment, because the price is still high and you expect the price to fall in the future. On the other hand, if you expect the shares of company X to rise, then it is beneficial to go long. In the future, you may make more profit when selling the CFD transaction, because you expect the price to rise. For both the long and short position, it applies that you can make a profit or a loss at the moment you close the position.
The leverage
When trading CFDs, you are dealing with leverage . This means that when you start trading CFDs, you do not have to pay the full costs right away. This means that you can take a larger position on the CFD market than you can actually pay with your capital. In addition, you can make a large profit in a short time by using leverage.
Unfortunately, this also means that you can quickly make a loss in a short period of time. Of course, you must be able to absorb this loss with your capital. Therefore, take a good look at the size of the leverage and be sure that you are trading with money that you can afford to lose.

De 4 basisprincipes van het handelen in CFD’s!
Wanneer je begint met het handelen in CFD’s krijg je met verschillende basisprincipes te maken: spreads, handelsgrootte, tijdsduur en winst en verlies. Het is verstandig dat je goed weet wat deze principes inhouden, zodat je je risico kan beperken. Hieronder zijn de verschillende basisprincipes kort uitgelegd:
Spreads
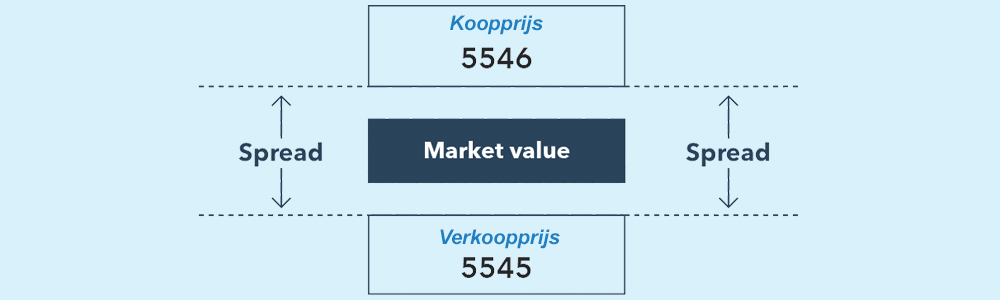
Één van de dingen waar je mee te maken krijgt wanneer je begint met CFD trading zijn spreads. Je hebt bij CFD’s twee verschillende prijzen, namelijk de prijs die je moet betalen wanneer je een CFD-transactie koopt en de prijs die je ontvangt wanneer je jouw CFD-transactie verkoopt. De verkoopprijs wordt ook wel de biedprijs genoemd. Voor deze prijs kun jij je CFD-transactie dus verkopen, voor deze prijs kun je een CFD short positie openen.
Bij het kopen van een CFD-transactie moet jij natuurlijk een bepaalde prijs betalen, de koopprijs. Dit wordt ook wel de laatprijs genoemd. Hiermee kan je een CFD long positie openen.
Tussen de bied- en laatprijs zit een verschil. Dit verschil tussen deze verkoopprijs en de koopprijs wordt ‘spread’ genoemd. De spreads zijn veelal ook meteen de kosten die je moet betalen. Vaak zijn deze spreads dynamisch worden de prijzen dus constant aangepast.
Trade size
When trading CFDs, standard contracts are often used. The size of this contract depends on the underlying value that the contract is about. For example, do you want to trade in silver? Then a standard contract is usually used, using 5000 troy ounces. In this way, there are different (standard) contracts for each underlying value.
Duration
When you enter into a CFD contract, this contract is often for an indefinite period. The position is often terminated when you decide to sell the CFD transaction. Do you have 200 silver contracts? Then this position is terminated because you decide to sell the 200 silver contracts. CFD trading is often seen as short-term investing .
If you leave a CFD position open beyond the closing time, you will be charged an overnight fee. You pay this fee because the broker has essentially financed you to open the position with leverage.
Have you entered into a term contract? The name says it all: then the contract does have a term attached to it. This means that the term contract is automatically terminated after the expiry date.
Profit and loss
How is the profit and loss of your transaction determined? The profit and loss is determined by multiplying the number of contracts you have by the value of the contract. Then you are not finished yet, because you then have to multiply this answer by the difference (closing price – opening price). Then you can subtract the additional costs that you made with the transaction (such as overnight costs).
The step-by-step plan is as follows:
- See how many contracts you have
- Multiply this number of contracts by the value of each contract
- Calculate the closing price – the opening price
- Multiply the answer from step 2 by the answer from step 3
- Subtract the additional costs you incurred from the answer in step 4
- Done! You have calculated your profit (return) , or unfortunately your loss
The different types of instruments you can choose when trading CFDs
There are many different categories to choose from when you want to start trading CFDs. The most well-known category is CFD share trading.
CFD stock trading
When you want to start trading CFD shares, your profit or loss is determined by the difference between the value at the moment you start the trade and at the moment you close the trade. This is also called the opening price and the closing price.
The big difference between CFD share trading and (traditional) share trading itself is that when trading in shares, you actually own the shares. With CFD share trading, you trade in the prices and not in the shares themselves. With CFD share trading, you can use leverage, which means you do not necessarily have to pay the full costs. This can mean that you have a greater underlying value than your assets can actually pay. When trading in shares yourself, you have to buy the shares yourself and pay all costs first, before you receive the shares. When trading in shares yourself, you must therefore have the full assets to buy the shares. In addition, with CFDs on shares you can respond to both price increases and decreases. This is not possible with (traditional) share trading.
CFD trading in indices
In addition to CFD stock trading, you can also choose to start with CFD trading on indices . With indices, no individual shares are traded but an entire stock index is traded. This can cause the leverage effects to be higher than when you trade in individual shares. If you want to start with CFD trading in indices, you can choose to start with the most traded American indices or to start with the most popular indices that you are interested in. Think of indices such as the Dutch AEX or the American NASDAQ.
CFD trading in commodities
You can also opt for CFD trading in commodities . This is the perfect opportunity if you are interested in the gold and oil industry. The commodities that are traded the most are gold, silver and oil. But with this construction you can trade in almost every conceivable commodity. You can also respond to rising and falling commodity prices.
CFD trading in the currency market
Are you interested in the currency market ? Then it is also possible to trade in it with regard to CFDs. If you want to start CFD trading in currencies , this is also called Forex trading . You can choose any available currency you want, for example the Euro or the Dollar. Forex trading is always done in pairs, such as EUR/USD. The Forex market is one of the largest markets in the world and is also one of the most traded CFD instruments.

CFD bond trading
CFD trading in bonds is less common. This does not mean that you cannot opt for it. Well-known bonds are the Bund, the T Note and the T Bill.
De CFD-handel in cryptocurrencies
The last category you can choose when you want to start CFD trading are cryptocurrencies . This is a bit like a currency, but cryptocurrencies are not physical forms of money. Cryptocurrencies are digital means of payment, for example Bitcoin , Litecoin, Ripple and Ethereum. These cryptocurrencies can rise and fall quickly compared to currencies, which makes CFD trading in cryptocurrencies very risky (of course, you have to deal with risks with every type of CFD trading). Interested in trading in Bitcoin, read more about Bitcoin CFD here .
To limit the risk, you can opt for good risk management . This risk management ensures that the losses are limited to some extent. An example of this risk management is the stop loss system. With this system, the order is automatically terminated if the price falls below a certain minimum or maximum value.
Is CFD trading for me?
Trading CFDs involves many risks. Always keep this in mind, because the threshold for CFD trading is very low. For example, anyone over the age of 18 can start trading in this way. CFD trading is particularly interesting for traders who want to expand their portfolio and keep the content varied. Because CFDs can rise and fall quickly, this type of trading is perfect for day traders. In CFD trading, profits and losses are mainly determined by market movements . CFD trading is therefore very interesting for investors who find it interesting to focus on this and to make decisions based on these market movements.
With CFD trading, you can own a higher underlying asset than you can actually own with your capital. Unfortunately, this does mean that when you make losses, you have to be able to absorb these losses with your capital.
If you want to start investing in CFDs, simply compare all CFD brokers and open an account today!